Bluetooth Network Security
Published on Nov 23, 2015
Abstract
Wireless communications offer organizations and users many benefits such as portability and flexibility, increased productivity, and lower installation costs. Wireless local area network (WLAN) devices, for instance, allow users to move their laptops from place to place within their offices without the need for wires and without losing network connectivity.
Ad hoc networks, such as those enabled by Bluetooth, allow users to:
Data synchronization with network systems and application sharing between devices.
Eliminates cables for printer and other peripheral device connections.
Synchronize personal databases.
Provide access to network services such as wireless e-mail, Web browsing, and Internet access.
However, risks are inherent in any wireless technology. The loss of confidentiality and integrity and the threat of denial of service (DoS) attacks are risks typically associated with wireless communications. Specific threats and vulnerabilities to wireless networks and handheld devices include the following:
All the vulnerabilities that exist in a conventional wired network apply to wireless technologies.
Malicious entities may gain unauthorized access to an agency‟s computer network through wireless connections, bypassing any firewall protections.
Sensitive information that is not encrypted (or that is encrypted with poor cryptographic techniques) and that is transmitted between two wireless devices may be intercepted and disclosed.
Sensitive data may be corrupted during improper synchronization.
Data may be extracted without detection from improperly configured devices.
Security Aspects in Bluetooth
The Bluetooth-system provide security at two level-
At Link layer
At Application layer
Link layer security
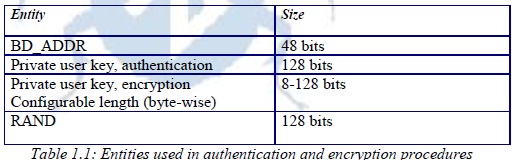
Four different entities are used for maintaining security at the link layer: a Bluetooth device address, two secret, keys, and a pseudo-random number that shall be regenerated for each new transaction.
The four entities and their sizes are summarized in Table-
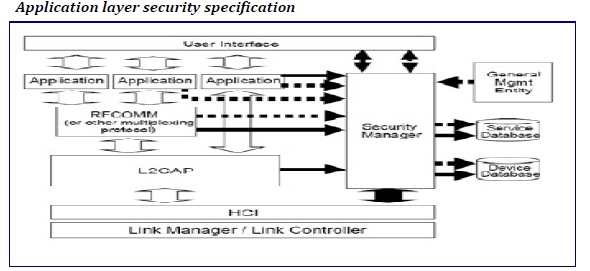
L2CAP: enforce security for cordless telephony.
RFCOMM: enforce security for Dial-up networking.
OBEX: files transfer and synchronization.
The encryption key in Bluetooth changes every time the encryption is activated, the authentication key depends on the running application to change the key or not. Another fact regarding the keys is that the encryption key is derived from the authentication key during the authentication process. The time required to refresh the encryption key is 228 Bluetooth clocks which is equal to approx. 23 hours. RAND or the random number generator is used for generating the encryption and authentication key. Each device should have its own random number generator. It is used in pairing (the process of authentication by entering two PIN-codes) for passed keys in the authentication process.
Security modes in Bluetooth
In Bluetooth there are three security modes which are:
Mode 1: Non-secure.
Mode 2: Service level security
Trusted device
Un-trusted devices
Unknown devices
Mode 3: Link level.
The trusted device is a device that has been connected before, its link key is stored and it‟s flagged as a trusted device in the device database. The un-trusted devices are devices that have also previously connected and authenticated, link key is stored but they are not flagged as a trusted devices.
The unknown devices are the devices that have not connected before. In Bluetooth service level we have three type of service in regard to the security:
Services that need authentication and authorization: this is automatically granted to the trusted devices but for the un-trusted devices manual authentication is required.
Services that need authentication only: in this case the authorization process is not necessary.
Attack Tools & Programs
Hardware Used: Dell XPS, Nokia N95, Nokia 6150, Hp IPAQ HX2790b.
Operating Systems: Ubuntu, Backtrack, Windows Vista, Symbian OS, windows mobile.
Software used: Bluebugger, Bluediving, Bluescanner, Bluesnarfer, BTscanner, Redfang, Blooover2, Ftp_bt.
Dell laptop with windows vista to be broken into and for scanning then with Linux to attempt attacks. Pocket pc for being attacked, and one mobile for attacking one for being attacked.
More Seminar Topics:
Embedded Web Technology, Embedded System in Automobiles, Electrooculography, Electronic Toll Collection, Electronic Counter-Countermeasures, Electro Dynamic Tether, Easy-To-Swallow Wireless Telemetry, Earthing Transformers For Power Systems, Distributed COM, Direct Current Machines, DD Using Bio-robotics, Data Loggers, Concentrating Collectors, Clos Architecture in OPS, Chip MorphingRelated Seminar Topics
- Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Miniature RF Technology Demonstration
- Secure Electronic Voting System Based on Image Steganography
- Securing Underwater Wireless Communication Networks
- Security In Embedded Systems
- Third Generation Solid State Drives
- Face Recognition Using Neural Network