SATRACK
Published on Dec 06, 2015
Abstract
According to the dictionary guidance is the 'process of guiding the path of an object towards a given point, which in general may be moving'. The process of guidance is based on the position and velocity if the target relative to the guided object.
The present day ballistic missiles are all guided using the global positioning system or GPS.GPS uses satellites as instruments for sending signals to the missile during flight and to guide it to the target.
SATRACK is a system that was developed to provide an evaluation methodology for the guidance system of the ballistic missiles. This was developed as a comprehensive test and evaluation program to validate the integrated weapons system design for nuclear powered submarines launched ballistic missiles.this is based on the tracking signals received at the missile from the GPS satellites. SATRACK has the ability to receive record, rebroadcast and track the satellite signals.
SATRACK facility also has the great advantage that the whole data obtained from the test flights can be used to obtain a guidance error model. The recorded data along with the simulation data from the models can produce a comprehensive guidance error model. This will result in the solution that is the best flight path for the missile.
The signals for the GPS satellite navigation are two L-band frequency signals. They can be called L1 and L2.L1 is at 1575.42 MHz and L2 at 1227.60 MHz.The modulations used for these GPS signals are
1. Narrow band clear/acquisition code with 2MHz bandwidth.
2. Wide band encrypted P code with 20MHz bandwidth.
L1 is modulated using the narrow band C/A code only. This signal will give an accuracy of close to a 100m only. L2 is modulated using the P code. This code gives a higher accuracy close to 10m that is why they are encrypted. The parameters that a GPS signal carries are latitude, longitude, altitude and time.
The modulations applied to each frequency provide the basis for epoch measurements used to determine the distances to each satellite. Tracking of the dual frequency GPS signals provides a way to correct measurements from the effect of refraction through the ionosphere. An alternate frequency L3 at 1381.05MHz was also used to compensate for the ionospheric effects.
GPS SIGNALS
The signals for the GPS satellite navigation are two L-band frequency signals. They can be called L1 and L2.L1 is at 1575.42 MHz and L2 at 1227.60 MHz.The modulations used for these GPS signals are
1. Narrow band clear/acquisition code with 2MHz bandwidth.
2. Wide band encrypted P code with 20MHz bandwidth.
L1 is modulated using the narrow band C/A code only. This signal will give an accuracy of close to a 100m only. L2 is modulated using the P code. This code gives a higher accuracy close to 10m that is why they are encrypted. The parameters that a GPS signal carries are latitude, longitude, altitude and time. The modulations applied to each frequency provide the basis for epoch measurements used to determine the distances to each satellite. Tracking of the dual frequency GPS signals provides a way to correct measurements from the effect of refraction through the ionosphere. An alternate frequency L3 at 1381.05MHz was also used to compensate for the ionospheric effects.
SATRACK CONCEPT
Guidance system evaluation concept of very early weapons systems depended on the impact scoring techniques. This means that the missile was shot and the accuracy was formulated on the scoring or the target destruction. This evaluation method was unacceptable for evaluating the more precise requirements of the latest systems. A new methodology was needed that provided insights into the major error contributors within the flight-test environment. The existing range instrumentation was largely provided by radar systems. They however did not provide the needed accuracy or range in the broad ocean test ranges. The accuracy projections needed to be based on the high confidence understanding of the underlying system parameters. SATRACK was developed with the necessary hardware and telemetry stations.
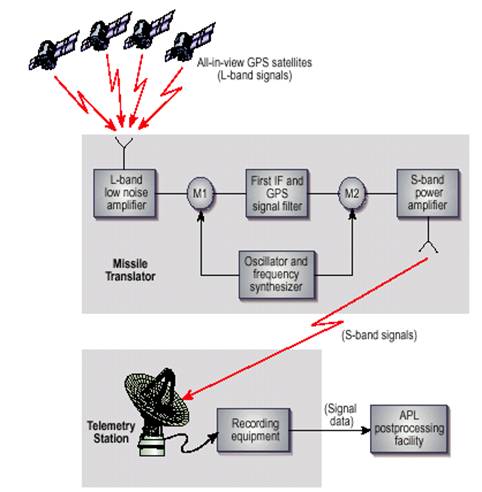
The figure shows the SATRACK measurement concept. The main parts are the GPS satellites, the missile translator and ground telemetry stations. The missile receives the signals from the GPS satellites. They are translated to another frequency and relayed to the ground telemetry stations. The telemetry station records the data for playback and for post processing.
The satellite signals received at the missile are translated to S-band frequencies for the telemetry station using the missile hardware called translators. The ground based telemetry station record the data after reception through the antenna after digitising the signals. Some ground sites uses L1 C/A signals to provide real time tracking solutions.
GPS TRANSLATOR
This flight hardware is fixed in the missile. The translator receives the GPS signals and they are amplified, shifted to an intermediate frequency, filtered to cover the satellite signal modulation bandwidth, shifted to an output frequency. Then they are amplified for transmission to one or more ground stations.